
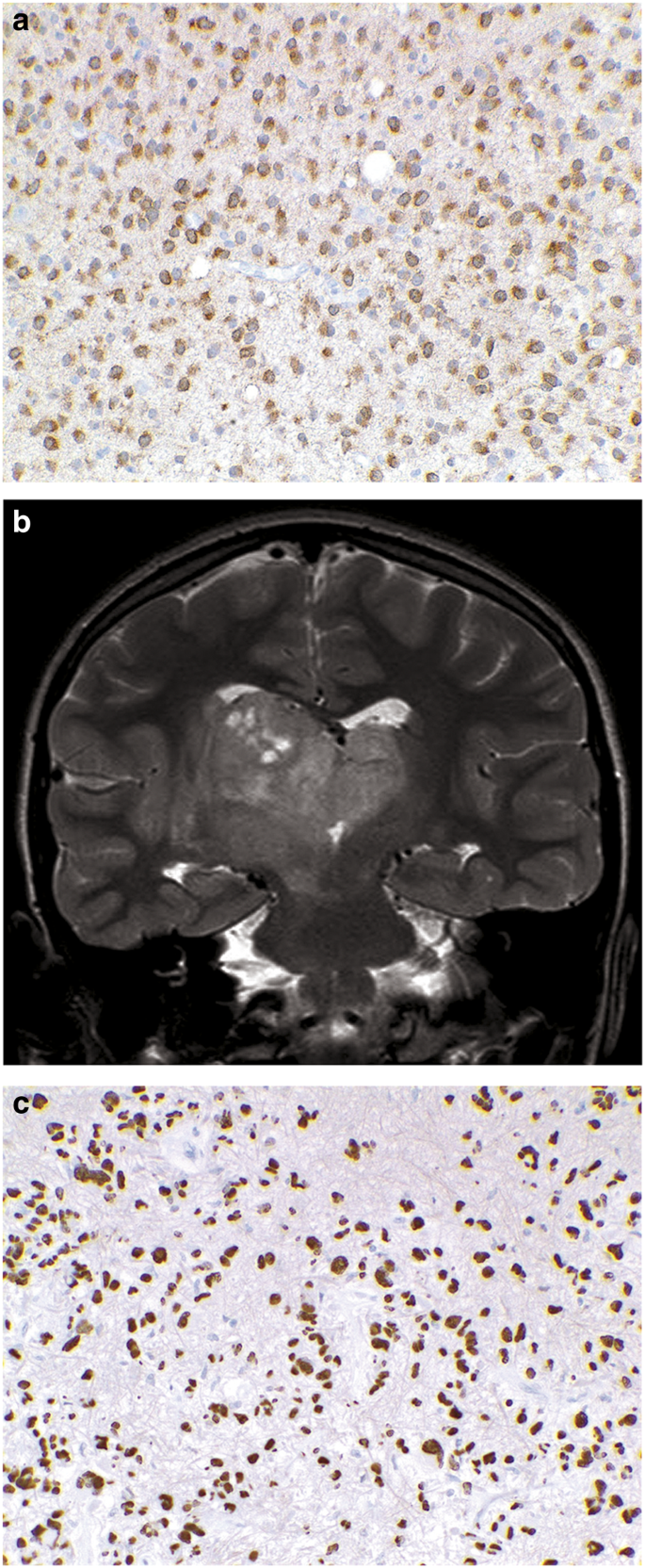
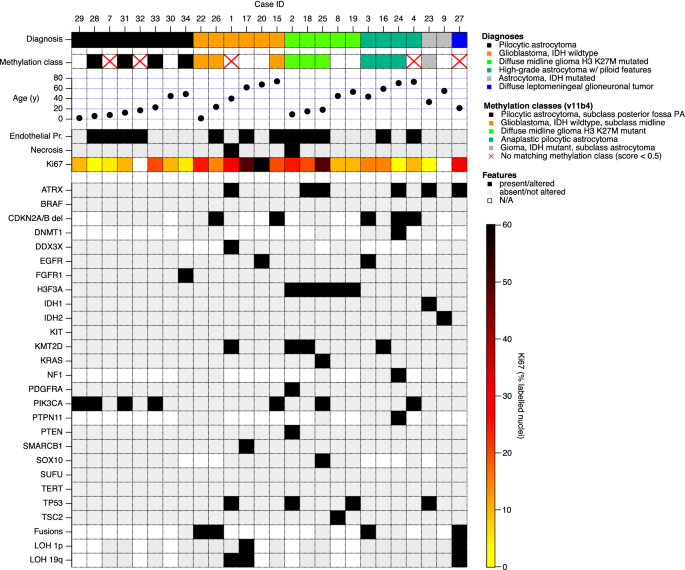
Much progress has thus been made by translating the most relevant molecular knowledge into a more precise clinical diagnosis of CNS tumors. In 108 biopsies reported across 13 studies, pathology showed 37 anaplastic astrocytomas (WHO grade III), 27 glioblastoma (WHO grade IV), 20 diffuse astrocytomas (WHO grade II), 3 anaplastic oligoastrocytomas (WHO grade III), 1 oligoastrocytoma (WHO grade II), 1 oligodendroglioma (WHO grade II), 15 malignant gliomas NOS, and 4 undefined tumors. Additionally, genome-wide methylation profiling is a very promising new tool in CNS tumor diagnostics. DIPGs represent a varied histological spectrum. Immunohistochemistry is a helpful alternative for further molecular characterization of several of these tumors. (PubMed, J Clin Neurosci) The present study suggests that adult cAA constitute a group of gliomas with relatively higher rate of IDH-1 mutations and prognosis similar to supratentorial AA. Molecular characteristics are also important for the diagnosis of several other CNS tumors, such as RELA fusion-positive subtype of ependymoma, atypical teratoid rhabdoid tumor (AT/RT), embryonal tumor with multilayered rosettes, and solitary fibrous tumor/hemangiopericytoma. Cerebellar anaplastic astrocytoma in adult patients: 15 consecutive cases from a single institution and literature review. Medulloblastomas, the most frequent embryonal CNS tumors, are divided into four molecularly defined groups according to the WHO 2016 Classification: wingless/integrated (WNT) signaling pathway activated, sonic hedgehog (SHH) signaling pathway activated and tumor protein p53 gene ( TP53)-mutant, SHH-activated and TP53-wildtype, and non-WNT/non-SHH-activated. Defining molecular markers for diffuse gliomas are IDH1/IDH2 mutations, 1p/19q codeletion and mutations in histone H3 genes. 19 histologically defined anaplastic pilocytic astrocytomas showed similarities to reference methylation classes, and therefore, grouped within these classes in the t-SNE. 83 of the histologically defined anaplastic pilocytic astrocytomas (colored in black) formed one group intermixed by only few other cases and were designated as DNA methylation class anaplastic astrocytoma with piloid features (MC AAP). Initial presenting symptoms most commonly are. For this analysis, the 20,000 most variably methylated CPG sites were used. In the United States, the annual incidence rate for Anaplastic astrocytoma is 0.44 per 100,000 people Signs and symptoms.
#ANAPLASTIC ASTROCYTOMA VERSUS DMG UPDATE#
This review provides an update of the most important diagnostic and prognostic markers for state-of-the-art diagnosis of primary CNS tumors. Anaplastic astrocytoma is a rare WHO grade III type of astrocytoma, which is a type of cancer of the brain. This combined ‘histo-molecular’ approach allows for a much more precise diagnosis of especially diffuse gliomas and embryonal CNS tumors. Since the update of the 4th edition of the WHO Classification of Central Nervous System (CNS) Tumors published in 2016, particular molecular characteristics are part of the definition of a subset of these neoplasms.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
